Imagine if retail stores checked each customer walking in as if they were going to steal something, or every movie theater checked your pockets and bags for smuggled in goods. Yes, this might be a slight burden to the customers, but at the end of the day the business would see higher profits which in turn could lower prices for consumers. Now what if something similar could be done for cloud businesses large and small alike, automatically protecting them without the need for physical security (or in this case IT staff) watching over their domain, both increasing profits and lowering costs? Microsoft’s Zero Trust Model redefines the concepts of identity and access management utilizing the cloud model for in office, virtual, and hybrid work scenarios.
What is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is like a security guard watching over your property 24/7/365. Anyone who attempts to enter the area is immediately thought to be a potential intruder, and unless they can show proper credentials, they are ousted from the area.
“Instead of believing everything behind the corporate firewall is safe, the Zero Trust model assumes every request is a breach in security, and verifies each request as though it originates from an unsecured network.”
Zero Trust works on the principal of ‘never trust, always verify’, meaning that every time a user signs into their mail client, business apps, or other linked accounts, they are treated as if they are a potential security threat. Utilizing Zero Trust means that all sessions must have end-to-end encryption, which can then be used to drive analytics for visibility, threat detection, and improved defenses. In this model, every access request is authenticated, authorized within policy constraints, and inspected for anomalies BEFORE granting access. That is already 3 layers of security before users even log in.
How does it work?
Zero Trust is a method of security that allows for businesses of all sizes to reduce the risk of a large data breach by applying micro-segmentation and least privileged access to minimize lateral movement within the domain; if a breach does occur, the whole organization is not necessarily at risk. Micro-segmentation is the process to create secure zones to separate workloads, each of which can be secured, like having panic rooms in several different areas of your house. If an intruder breaks in, they only have access to the area that they broke into instead of the whole house.
A Zero Trust Model has three aspects:
- Signals that inform decisions
- Zero Trust considers many sources of data to make informed decisions about whether a user should be admitted or not. Sources include identity systems (like Microsoft Authenticator) and device management and security tools
- Policies that make access decisions
- Access requests and signals are analyzed to deliver an access decision based on specific access policies that provide granular, organization wide access control
- Enforcement capabilities
- Decisions are enforced across the cloud, such as read only access to SaaS apps, or fixing compromised passwords with self-service password resets
Why Use Zero Trust?
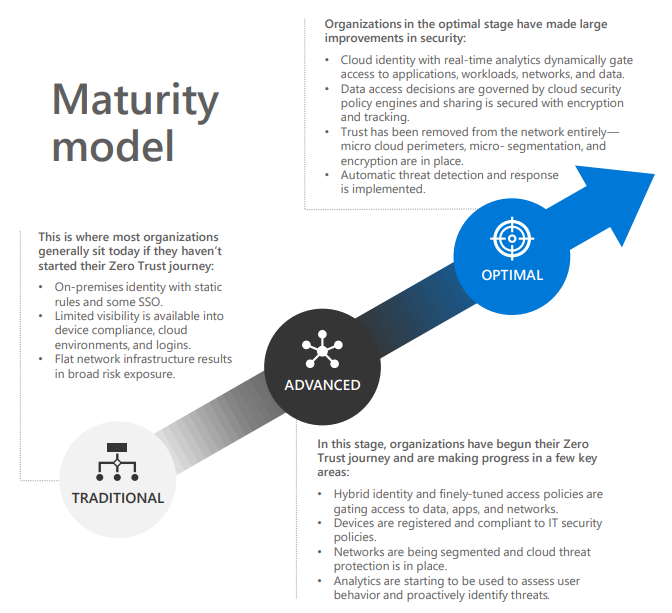
The Zero Trust model is designed specifically for work-from-anywhere scenarios. Traditionally, all users log in from the same location, in the same office, every day. With work-from-anywhere becoming more and more prominent, businesses need to keep up with the ever-changing access points, locations, and devices.
An employee that used to come into the office 5 days a week, worked on a company device, and had a set schedule now works from 3 different locations on an alternating schedule with a mix of personal and company devices. Utilizing traditional IT principals, this single employee would need a laundry list of whitelisting’s, remote access devices, and VPN’s. With Zero Trust, this employee’s location, device, and time zone can all be learned by AI, and be independently verified.
Implementation
You might want to consider implementing Zero Trust policies if: Your business is a cloud/hybrid model or if it plans to be, if your employees can bring their own devices to work, if your employees work from home, or if organizational assets, resources, and data are being accessed from outside the corporate network.
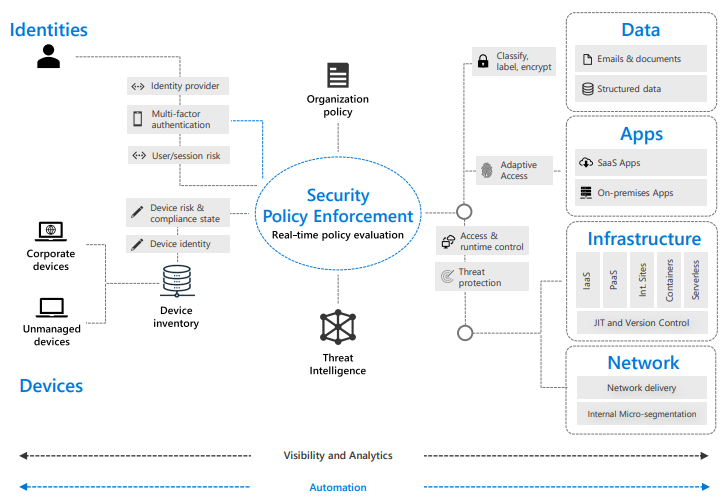
Zero Trust must be built into six foundational elements for implementation to be successful. These elements include identities, devices, applications, data, infrastructure, and networks. Each element is a source of a signal which allows for Zero Trust to decide whether the request for data is valid or not. If the system decides that the request is valid, you are signed in successfully. If the system denies the request, the user is unable to log in and a record is created to prevent a breach both when the request is denied, as well as in the future.
As you think about your Zero Trust readiness, consider these key investments to drive a successful implementation:
- Strong Authentication: Require MFA and session risk detection as the backbone for your access strategy to minimize identity compromise
- Policy-based adaptive access: Define access policies for resources and enforce them consistently with a security policy engine that provides both governance and insight into variances
- Micro-Segmentation: Move beyond simple centralized network-based perimeter to comprehensive and distributed segmentation using software-defined micro-perimeters
- Automation: Automated alerting and remediation to reduce mean time to respond (MTTR) to attacks
- Intelligence and AI: Utilize cloud intelligence and all available signals to detect, monitor, and respond to access anomalies in real time
- Data Classification: Discover, classify, protect, and monitor sensitive data to minimize exposure from malicious or accidental exfiltration
For more information about how Zero Trust can help your business, please schedule a free consultation at Finchloom.com.